Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a prevalent condition in men and its incidence rate increases with age. BPH requires treatment when the patients begin experiencing lower urinary tract symptoms, affecting their quality of life.The prostate is a small gland in the male genital tract that, aside from being a reproductive organ, plays a significant role in male urination. Prostatic muscle contraction causes to slow the urinary flow.
The BPH symptoms include the feeling of bladder fullness even after voiding, urination urgency, weak urine flow, experiencing difficulty in starting or stopping urination, and the need to strain or push to urinate. In severe BPH cases, the patient may even become unable to urinate, which is considered a medical emergency and requires immediate intervention.
Diagnosis involves prostatic specific antigen (PSA) testing, digital rectal exam (DRE), and screening with sonography.
BPH treatment
Alpha-blockers
The first class of drugs used for BPH treatment is alpha-blockers which act by causing the relaxation of smooth muscle at the prostate and bladder, improving the urinary flow rate and alleviating urethral obstruction. This class of drugs is efficacious in improving urinary symptoms and BPH, although they do not affect prostatic size reduction. One benefit of alpha-blockers, such as alfuzosin, terazosin, and tamsulosin, is their rapid effectiveness. Their adverse effects include dizziness, impaired ejaculation, and hypotension.
5-alpha reductase inhibitors
5-alpha reductase inhibitors (5ARIs), including finasteride and dutasteride, are another class of drugs with therapeutic applications for BPH treatment. These drugs are indicated for BPH patients with moderate to severe symptoms, a prostate volume (PV) of ≥ 30 cc, and a PSA test of ≥ 1.5 cc. They contribute to a decrease in dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and PSA levels and improve urinary flow. A comparison between finasteride and dutasteride regarding their effectiveness verified the superior efficacy of the latter drug. According to recent studies and data, the sexual side effects of the two drugs are somewhat similar, although these side effects are occasionally lower for dutasteride.
Combination therapy with alpha-blockers plus 5ARIs
According to various studies, combination therapy with tamsulosin and dutasteride can be effective in the treatment of BPH patients with moderate to severe symptoms, a prostate volume (PV) of ≥ 30 cc, and a PSA test of ≥ 1.5 cc [1, 6]. This kind of treatment can reduce the number and frequency of prescribed drugs for patients. Clinical trials have established the synergistic effect and dual mechanism of action of these two drugs, demonstrating significant superiority to monotherapy with either tamsulosin or dutasteride in alleviating the symptoms and reducing the clinical progression of BPH in men. In addition, combination therapy is associated with a decreased likelihood of urinary retention and risk of surgery in patients [2]. The recent 2021 guidelines and articles strongly recommend the use of this treatment regimen in BPH patients [6].
In a study by Hailot et al., the use of combination therapy (with tamsulosin plus dutasteride) compared to monotherapy (either tamsulosin or dutasteride) reduced the risk of acute urinary retention (AUR) and the need for BPH-related surgery. Moreover, the maximum urinary flow rate was significantly higher in patients receiving combination therapy than in those receiving individual monotherapy [3].
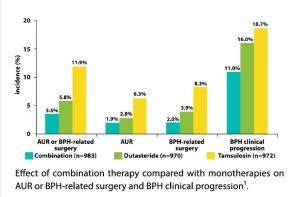
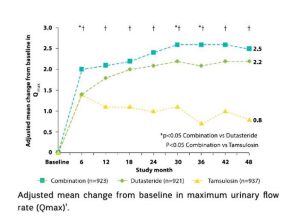
According to a study by Salvatore et al., timely and rapid use of combination treatment with tamsulosin plus dutasteride improves patient responsiveness and overall symptoms while reducing the progression of the BHP disease and the risk of AUR incidence [4].
Reference:
-
Roehrborn CG. Benign prostatic hyperplasia: an overview. Rev Urol. 2005;7(suppl 9):S3-S14.



